IoT gateways act as a gate or bridge between the edge devices, sensors, equipment, systems, and the cloud. It sits at the intersection of edge computing systems, between the external internet and the local intranet in the ecosystem. Thus an IoT gateway device is the key access point for network connectivity. If the IoT hubs encounter an attack, that will jeopardize the entire IoT ecosystem.
In order to prevent any data tampering or unrestricted access, communications between the ‘things’ – the gateway and the cloud therefore must be secure. Security breaches on IoT products could have a variety of consequences like data privacy, economic damage, and public safety. These concerns emphasize the need to take a security-focused approach while building an IoT system. Next, how to secure a gateway will be discussed.
Secure an IoT Gateway
The IoT gateway is often the first to be attacked in the IoT system because of two reasons: (1) Gateways often have a higher processing power, which can use to run more intensive applications. More power means power software, but powerful software means more vulnerabilities for a hacker to exploit. (2) Because of its location as an edge device between the internet and the intranet, the gateway is the point of entry for any threat vector.
The types of vulnerability can be divided into four areas: communication, physical, lifecycle, and software. Communication attacks can put the data transmitted between IoT devices and servers at risk. Physical attacks target the chips in the IoT devices directly. Attacks on the device software are also common. Lifecycle attacks put the integrity of the IoT device as it changes hands from user to maintenance. For designing IoT gateways, more emphasis should be first put on communication attacks, as an IoT gateway performs several critical functions from translating protocols to encrypting, processing, managing and filtering data. Besides, the physical attack is also a concern.
Communication Security
As stated above, IoT gateways aggregates sensor data translate between sensor protocols, process sensor data before sending it onward, and more, communication security should be considered first. Attackers can try multiple means to intercept, spoof or disrupt messages sent from devices back to the server. Cryptography technologies are often used to combat communication attacks and preserve confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity which are the three key principles of security. Designers need to ensure that all communications between the gateway and devices are meeting each of the three principles while communication is happening in the internal and external networks. Figure 1 shows that providing complete IoT security not only requires that the communication from the gateway to the cloud is secure, but requires that the gateway can participate in the secure communication and management of connected edge node devices, which themselves must be secured.
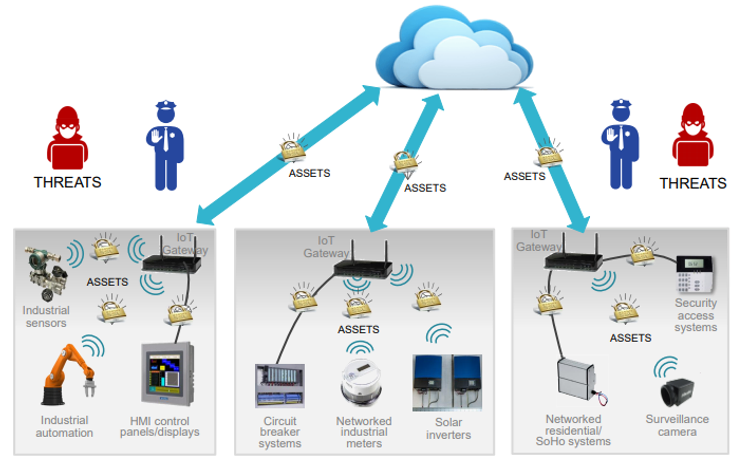
Securing the IoT gateways’ communication
As a typical IoT device is resource-constrained, information is exchanged in plain text. For most IoT applications, this information is the most valuable component. It’s very easy for an unauthorized or undesired person to eavesdrop on this valuable information due to which data exchange is no longer confidential.
To ensure data confidentiality, while information is exchanged between server and client, encryption is commonly used. Using encryption, the transmitter converts the confidential information into seemingly random bytes with the help of a secret key before sending it over the internet.
Only the receiver has the means that is the secret key to convert these random bytes or encrypted data back into the original data. Dusun’s IoT Gateways support common encryption algorithms such as DES, RSA, AES, etc.
Besides, Dusun’s smart gateways are programmable which lets customers make their programs to use their security mechanism.
To ensure data integrity, hashing is the most commonly used method. This is achieved by the transmitter converting variable-length data into random bytes of fixed length. The actual data and these random bytes are sent over the internet.
After receiving this information, the receiver also converts the variable-length data into random bytes using the same method that was used at the source. The random bytes calculated by the receiver match those that were sent.
Then the receiver knows that the data has not been tampered with. If they don’t match, then someone tampered with either the data or the random bytes, and the receiver knows that the information cannot be trusted. Dusun’s IoT Gateways support common cryptographic hash functions such as MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, etc.
Authentication devices and services must use cryptographic certificates to prove they are who they say they are. Dusun’s IoT Gateways support WIFI, BLE, ZigBee, and Z-Wave. We use WPA2 authentication for WIFI, and use AES-CCM for BLE, Z-Wave, and ZigBee.
It is imperative that the IoT verifies the authenticity of the server before it starts exchanging valuable information. A common method used to authenticate a server is to request and verify the TLS or SSL certificate of the server.
Transport layer security, abbreviated as TLS, is a security protocol that sits between the transport layer and application layer of TCP/IP protocol. TLS or SSL uses a combination of the above standard methods to create a secure connection between an IoT device and a cloud server that enables the exchange of data securely.
Standard IoT protocols that are based on TCP such as MQTT can also use TLS to do encrypted communication. Dusun’s smart gateways support TLS/SSL when communicating with cloud servers.
Physical Security
Silicon attacks are often split into two categories: non-invasive and invasive. Non-invasive (side-channel) use different ways to try to observe the chip to gain information. These include perturbation techniques–altering the power supply voltage or interfering with electromagnetic signatures. Invasive techniques involve opening the chip to probe or modify part of the passivation layer.
Protecting saved data in the gateways chips is very important. In the first step, we should not let the data saved in flash or EEROM be fetched without permission. Then the data saved in the ram when the system running is also should be protected.
The common way is to use chips with physical counter-measures such as ARM’s SecurCore. Dusun adopts chips with security measures for the data storage including key storage in EEPROM, using chips containing MPU for memory protection, etc.
Summary
IoT security includes both physical device security and network security. As a data transfer device, the safety of IoT gateways is very important in the IoT system. For physical security, the chips for saving data and holding data should be protected by hardware measures such as hardware keys, MPU, and others.
Communication security or network security should be put more emphasis on. Cryptography technologies are commonly used to combat communication attacks to preserve data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity:
- l Data confidentiality means devices and services must use cryptographic encryption to protect data privacy in flight.
- l Data integrity devices and services must use cryptographic hashing to ensure data is not changed in flight.
- l Authentication devices and services must use cryptographic certificates to prove the identity.
For security reasons, Dusun’s IoT gateways take many known measures to counter communication and physical attacks. They support common encryption algorithms, hash algorithms, and authentication ways.
When communicating with the cloud server, transport layer security(TLS) is supported. And the programmable & open-source ability of smart gateways lets the user use their own encryption algorithms. Dusun uses chips with security measures to protect data safety saved in the hardware.



















