In an ideal environment, wireless communication satisfies the following formula:
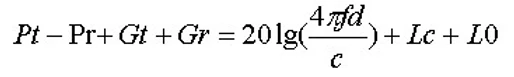
Pt —- the transmit power of the transmitter.
Pr —- the sensitivity of the receiver.
Gt —- transmit antenna gain.
Gr —- Receive antenna gain.
f —- carrier frequency.
d —- the distance between the receiving and transmitting antennas.
c —- speed of light (3 x 108m/s).
Lc —- Feeder insertion loss of the base station transmit antenna.
L0 —- Air propagation loss caused by the environment.
where p and c are constants, so the above formula is easily converted into the following procedure:
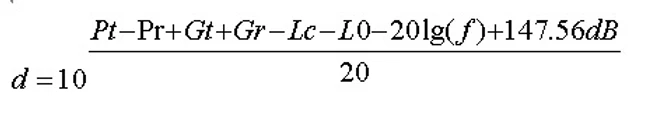
It can be seen from this formula that improving the receiving sensitivity can effectively increase the communication distance. For Lora, the performance of the antenna is critical. Ways to increase the communication distance include increasing the transmit power, increasing the gain of the transceiver antenna, reducing the insertion loss of the base station feeder, reducing the air propagation loss, and reducing the carrier frequency. Circumstances and regions limit the last two approaches, but selecting a high-performance antenna can achieve the other three.
Antenna Mechanism
A transmitter and a receiver are required for every type of wireless transmission, including LoRa. When Device A seeks to connect with Device B, it converts the data to be sent into a radio wave, which the transmitter subsequently broadcasts. This radio wave is subsequently received by Device B’s receiver, which demodulates it into data that an onboard computer can understand.
A LoRa antenna collaborates closely with the transmitter and receiver during the transmission and receiving processes. The transmitter sends an electrical signal to the antenna, which subsequently broadcasts the signal as radio waves. During the reception, an antenna intercepts a portion of the power from a radio wave, amplified by the receiver.
While antennas do not generate radio energy, they play an important function in diverting, directing, or focusing radio wave transmission. As a result, they can considerably improve both transmission range and quality, which may be just what your LoRa network needs. This directional trait, known as antenna gain, is a highly significant property of antennas.
Antenna Gain measures the degree of directivity of the antenna’s radiation pattern:
Directional antennas direct radio waves in a certain direction more than others, whereas omnidirectional antennas transmit and receive radio waves in all horizontal directions equally.
Thus, high gain antennas will allow you to achieve a longer range and higher signal quality in LoRa communication, but they must be pointed directly towards the receiving antenna. Although low-gain antennas have a shorter range, the direction of the antenna is less significant, making mesh networks easier to create. As a result, your antenna selection will be heavily influenced by the precise LoRa communication situation that you have in mind.
LoRaWAN Gateways
LoRa antennas, like LoRaWAN gateways, are classified as indoor or outdoor. Indoor antennas have lower gain and are smaller in size, making them appropriate for gateways with limited coverage. Outdoor antennas are larger, more robust, and have a higher gain.
Several outdoor gateways on the market:
LoRa Raspberry Pi Gateway
The LoRa Raspberry Pi Gateway is a professional-grade gateway with the hacker in mind. While other low-cost gateways are a single channel, the LoRa Raspberry Pi Gateway comes with a fully heatsinked concentrator capable of multi-channel, multi-node communication, all running in a friendly, hackable Raspberry Pi environment. The gateway includes a 2dBi 915MHz antenna and a multi-frequency GNSS(GPS) antenna. The Max TX power is 27dBm.
dlos8 outdoor LoRaWAN gateway
The DLOS8 is an open-source outdoor LoRaWAN Gateway. The DLOS8 uses a Semtech packet forwarder and is fully compatible with the LoRaWAN protocol. It includes an SX1301 LoRaWAN concentrator, which provides ten programmable parallel demodulation.
However, according to user feedback on the Amazon platform, they are not doing well with the antenna. From the data point of view, the antenna gain is not as good as other products of the price.
The things outdoor gateway
The Things Outdoor Gateway is manufactured by Browan Communications Inc and is
also known as the Browan Outdoor Micro Gateway. The Things Outdoor Gateway (TTOG) is an industrial, outdoor, and fully compliant gateway at a very low cost. The antenna Connection is N-Type. It has various antennae available for a 15km+ range. The TX power is up to 27 dBi.
MikroTik KNOT LR8 kit
KNOT LR8 kit is an out-of-the-box IoT Gateway solution for LoRa® technology. It uses Narrow. Band and CAT-M technology. Because of the low cost, low bandwidth cellular connection, it is supported by countless global mobile operators. This kit contains a pre-installed UDP packet forwarder to any public or private LoRa® servers. The antenna gain is 1.5 dBi.
SenseCAP Outdoor Gateway
SenseCAP Gateway for LoRaWAN is an IP66 industrial-grade outdoor product that supports an extended operating temperature range, making it applicable for low-power consumption, long-range data collection IoT scenarios like smart farming. Antenna gain is 2.5 dBi.
DUSUN Outdoor Gateway
DSGW-014 LoRaWAN gateway outdoor is based on the LoRaWAN protocol, with built-in Ethernet connectivity for a straightforward setup. Additionally, an onboard WiFi setup (supporting 2.4 GHz/5GHz WiFi) allows it to be easily configured via the default WiFi AP mode. With its industrial-grade components, it achieves a high standard of reliability. The TX power is up to 27dBm.
For outdoor LoRaWAN gateways, the environment is relatively harsh, while FRP has strong weather, corrosion, UV, aging, and impact resistance. Due to various complex environments, people are more inclined to choose fiberglass antennas for LoRaWAN gateways. Dusun outdoor gateway applies fiberglass antenna with high directivity and high efficiency. Coupled with its higher gain and TX POWER, it can effectively extend the communication distance and maximize the advantages of LoRa.
Several indoor gateways on the market:
Kerlink LoRaWAN indoor gateway
The IoT LoRaWAN gateway leverages the successful LoRa RF technical design and the common software of Wirnet i-Series gateways. In addition, it embeds built-in high rejection filters and secured Software architecture to be reliable gateways in the core of your smart application. Its antenna’s TX power is up to 27Dbm.
SEEED The Things Indoor Gateway
The Things Indoor Gateway(TTIG) is designed to be a fully compliant, ultra-low-cost LoRaWAN gateway, with WiFi as the backhaul. The gateway comes with a wall plug and can be powered over USB-C on 900mA, making the gateway even more suitable for applications that require dynamic coverage. Its antenna’s TX power is up to 27dBm.
Laird Sentrius RG1xx
Laird’s Sentrius™ RG1xx LoRa-Enabled Gateway is the ultimate in secure, scalable, and robust. Based on the Semtech SX1301/SX1257 chipset designs, it offers a LoRa range of up to ten miles and pre-loaded LoRa Packet Forwarder software, perfect for highly scalable, flexible IoT networks. According to its data sheet, the antenna gain is 2 dBi.
DUSUN Indoor Gateway
DSGW-090B LoraWAN Indoor Gateway is a robust 8-channel gateway. Adopting the SX1302 LoRa chip and secure crypto chip, DSGW-090B provides a high-efficiency and reliable connection.DSGW-090B has a line of sight up to 15 km and can cover about 2 km in an urbanized environment, covering larger areas and providing connectivity to more than 2000 nodes.
Its antenna gain is 2.44 dBi, and the max TX power is 27dBm. It’s worth mentioning that as a high-performance indoor gateway, it has a good antenna, but its price is only $299, which is lower than the price of most similar products.
Final Thought
Antennas are a key part of the RF chip. They are particularly important when choosing the best antenna for LoRa devices (such as LoRa nodes and LoRaWAN gateways) that transmit and receive data in the RF band. To ensure the quality of the antenna, choosing a cost-effective LoRaWAN gateway is a top priority for users.



















