Dusun gateways supports most protocols and allow users make their own programs which utilize these protocols such as MQTT to send data to clouds.
This article shows how to use Paho which contains open source MQTT client libraries to communicate with a MQTT broker.
Introduction
An IoT gateway/hub aggregates sensor data, translates between sensor protocols, processes sensor data before sending it to clouds. There are several protocols that IoT used for gateways communicating with clouds, including Message Queuing Telemetry Transport(MQTT),Constrained Application Protocol(CoAP), etc. MQTT is a publish-subscribe-based messaging protocol and becomes a very popular protocol for IoT to internet communication. Dusun gateways supports most protocols and allow users make their own programs which utilize these protocols such as MQTT to send data to clouds. This article shows how to use Paho which contains open source MQTT client libraries to communicate with a MQTT broker.
1. What is MQTT and PAHO
MQTT and its working principle
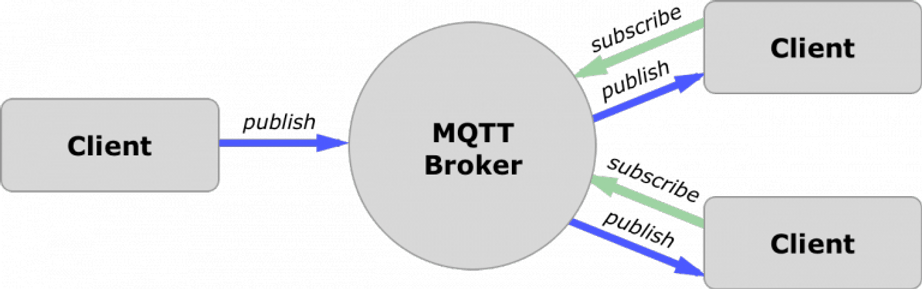
MQTT is a light-weight publish/subscribe messaging protocol, originally created by IBM and Arcom around 1998. It is designed as a lightweight messaging protocol that uses publish/subscribe operations to exchange data between clients and the server. Furthermore, its small size, low power usage, minimized data packets and ease of implementation make the protocol ideal of the “machine-to-machine” or “Internet of Things” world. MQTT server is called a broker and the clients are simply the connected devices. When a device (a client) wants to send data to the broker, we call this operation a “publish”. When a device (a client) wants to receive data from the broker, we call this operation a “subscribe”.
What is Paho
The Eclipse Paho project is rapidly becoming a source of some great MQTT clients. Eclipse Paho is an open-source implementation of MQTT client, available in various programming languages– currently it contains implementations in C, Java, JavaScript, Python (contributed from the mosquitto project), Lua, C++, embedded/minimal C, Go… and an Objective-C client is about to be added. Users can you Paho to send subscribe and publish messages to a MQTT broker such as mosquitto broker. Users can deploy Paho libraries on Dusun gateways and publish sensor data messages to their MQTT broker server. Then Dusun gateways publish the sensors’ state to the MQTT broker, user apps subscribe the topic and watch the sensor status remotely.
The procedure to write a Paho client library based application
- Create a client object
- Set the options to connect to an MQTT server
- Set up callback functions if multi-threaded (asynchronous mode) operation is being used.
- Subscribe to any topics the client needs to receive
- Repeat until finished:
- Publish any messages the client needs to
- Handle any incoming messages
- Disconnect the client
- Free any memory being used by the client
2.PAHO Client Code Samples
Paho project has provided some samples which can be revised to suit users needs. Paho_c_sub.c provides codes for subscribing MQTT topics, while Paho_c_pub.c is the code sample for publishing MQTT messages. MQTTClient_publish.c/ MQTTClient_subscribe.c are simple samples for publishing/ subscribing MQTT topics. For simplicity, MQTTClient_publish and MQTTClient_subscribe.c were used to explain the procedure of an MQTT Client.
1) MQTT Publish client
#define ADDRESS "tcp://localhost:1888" //broker address;
#define CLIENTID "ExampleClientPub"
#define TOPIC "my_topic" //MQTT topic name
#define PAYLOAD "{\"temperature\":20}" //message to be sent;
#define QOS 1
#define TIMEOUT 10000L
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
MQTTClient client;
MQTTClient_connectOptions conn_opts = MQTTClient_connectOptions_initializer;
MQTTClient_message pubmsg = MQTTClient_message_initializer;
MQTTClient_deliveryToken token;
int rc;
/*Create a client object*/
MQTTClient_create(&client, ADDRESS, CLIENTID,
MQTTCLIENT_PERSISTENCE_NONE, NULL);
/*Set the options to connect to an MQTT server*/
conn_opts.keepAliveInterval = 20;
conn_opts.cleansession = 1;
if ((rc = MQTTClient_connect(client, &conn_opts)) != MQTTCLIENT_SUCCESS)
{
printf("Failed to connect, return code %d\n", rc);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* publish a message to the topic */
pubmsg.payload = PAYLOAD;
pubmsg.payloadlen = (int)strlen(PAYLOAD);
pubmsg.qos = QOS;
pubmsg.retained = 0;
MQTTClient_publishMessage(client, TOPIC, &pubmsg, &token);
printf("Waiting for up to %d seconds for publication of %s\n"
"on topic %s for client with ClientID: %s\n",
(int)(TIMEOUT/1000), PAYLOAD, TOPIC, CLIENTID);
rc = MQTTClient_waitForCompletion(client, token, TIMEOUT);
printf("Message with delivery token %d delivered\n", token);
/* Disconnect the client*/
MQTTClient_disconnect(client, 10000);
/* Free any memory being used by the client*/
MQTTClient_destroy(&client);
return rc;
}
2) MQTT subscribe client
#define ADDRESS "tcp://localhost:1883" //broker address;
#define CLIENTID "ExampleClientSub"
#define TOPIC "my_topic" //MQTT topic name
#define PAYLOAD "Hello World!"
#define QOS 1
#define TIMEOUT 10000L
volatile MQTTClient_deliveryToken deliveredtoken;
void delivered(void *context, MQTTClient_deliveryToken dt)
{
printf("Message with token value %d delivery confirmed\n", dt);
deliveredtoken = dt;
}
/* received message callback function*/
int msgarrvd(void *context, char *topicName, int topicLen, MQTTClient_message *message)
{
int i;
char* payloadptr;
printf("Message arrived\n");
printf(" topic: %s\n", topicName);
printf(" message: ");
payloadptr = message->payload;
for(i=0; ipayloadlen; i++)
{
putchar(*payloadptr++);
}
putchar('\n');
MQTTClient_freeMessage(&message);
MQTTClient_free(topicName);
return 1;
}
/* Connection lost callback function*/
void connlost(void *context, char *cause)
{
printf("\nConnection lost\n");
printf(" cause: %s\n", cause);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
/*Create a client object*/
MQTTClient client;
MQTTClient_connectOptions conn_opts = MQTTClient_connectOptions_initializer;
int rc;
int ch;
MQTTClient_create(&client, ADDRESS, CLIENTID,
MQTTCLIENT_PERSISTENCE_NONE, NULL);
/*Set the options to connect to an MQTT server*/
conn_opts.keepAliveInterval = 20;
conn_opts.cleansession = 1;
/*Set callback functions*/
MQTTClient_setCallbacks(client, NULL, connlost, msgarrvd, delivered);
if ((rc = MQTTClient_connect(client, &conn_opts)) != MQTTCLIENT_SUCCESS)
{
printf("Failed to connect, return code %d\n", rc);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Subscribing to topic %s\nfor client %s using QoS%d\n\n"
"Press Q to quit\n\n", TOPIC, CLIENTID, QOS);
/* Subscribe to any topics the client needs to receive*/
MQTTClient_subscribe(client, TOPIC, QOS);
/*waiting Q/q key input to exit*/
do
{
ch = getchar();
} while(ch!='Q' && ch != 'q');
/* unsubscribe, disconnect and free the client*/
MQTTClient_unsubscribe(client, TOPIC);
MQTTClient_disconnect(client, 10000);
MQTTClient_destroy(&client);
return rc;
}
3. Test PAHO Clients
The Dusun gateway is based on Linux operating systems, then compiling the Paho project has little difference for Linux PC and Dusun gateways. Here we compile and test the Paho client on a Linux PC and then show how to compile the Paho client for the gateway whose cpu architecture is MIPS.
1) Compiling Paho MQTT client and test it on PC
Compiling Paho is easy on a Linux PC with the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/eclipse/paho.mqtt.c.git
cd paho.mqtt.c
make
sudo make install
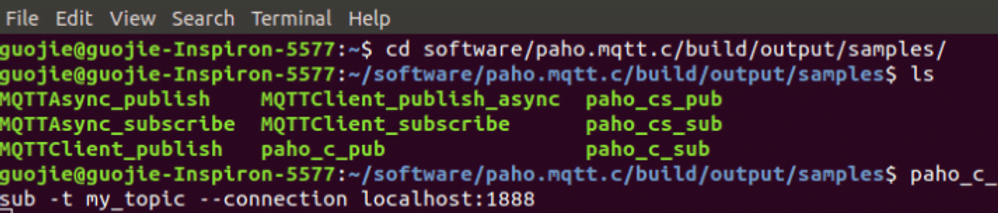
Then we can find the compiled binaries on ./build/output directory. In the ./build/output/samples directory, we can see the paho_c_pub/paho_c_sub and MQTTClient_publish/MQTTClient_subscribe which we described above and will be used for testing here.
We should install an eclipse mosquitto server before testing as the following commands:
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:mosquitto-dev/mosquitto-ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install mosquitto
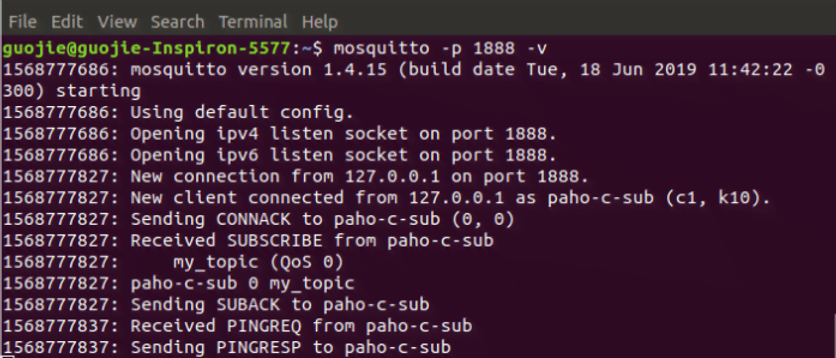
After the mosquitto is installed, we start the mosquitto broker (1888: port number);
Mosquitto –p 1888 -v
We test the paho client by starting the Paho clients, the figures below show the results:
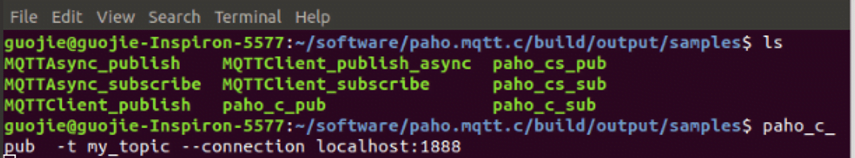
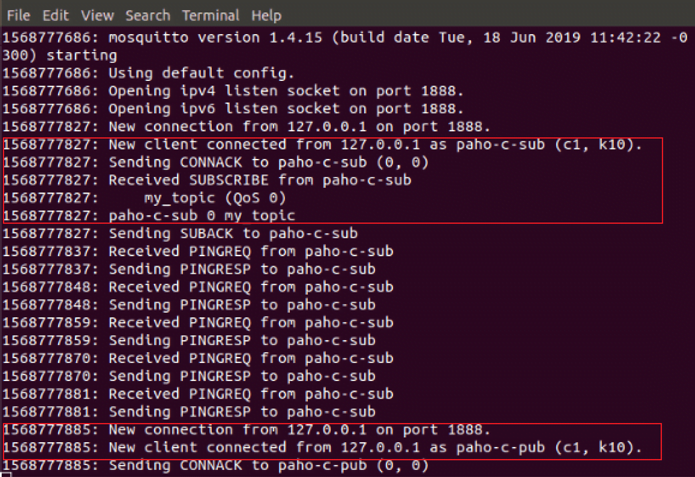
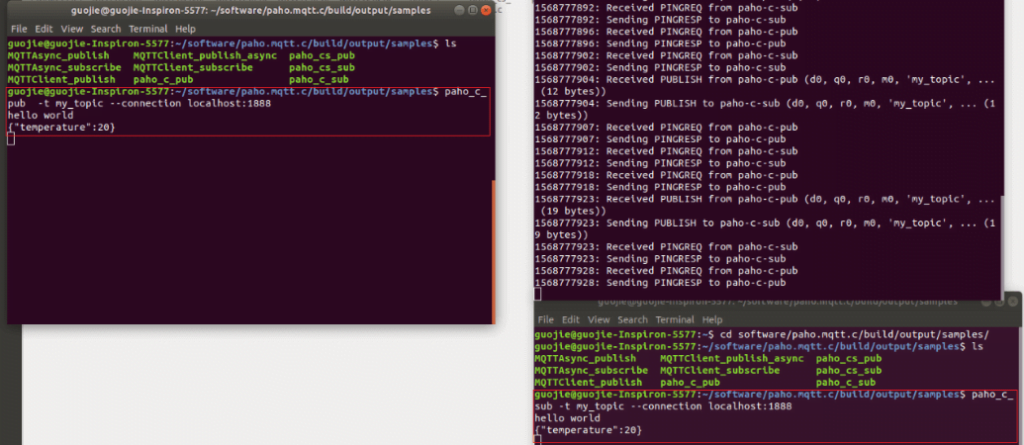
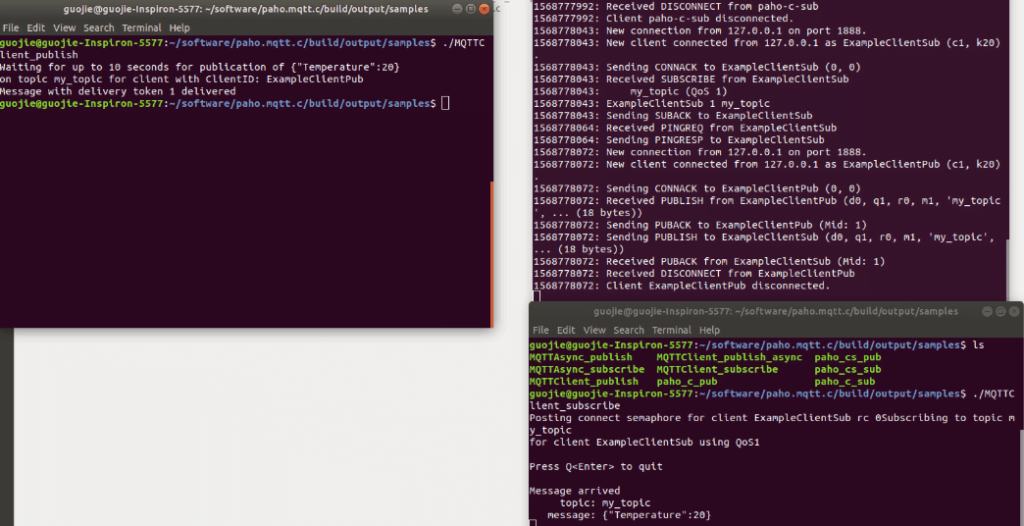
2) Cross compiling Paho MQTT client for Dusun gateway.
Revise the makefile in the Paho directory (e.g. /paho.mqtt.c): add the following lines, omit cc?=gcc in the file. you should change /OpenWrt-SDK to your OpenWrt SDK folder.
CC = ./OpenWrt-SDK/staging_dir/toolchain-mipsel_24kec+dsp_gcc-4.8-linaro_uClibc-0.9.33.2/bin/mipsel-openwrt-linux-gcc
CFLAGS = -I /OpenWrt-SDK/staging_dir/target-mipsel_24kec+dsp_uClibc-0.9.33.2/usr/include
LDFLAGS =-L/OpenWrt-SDK/staging_dir/target-mipsel_24kec+dsp_uClibc-0.9.33.2/usr/lib -L/home/guojie/Software/OpenWrt-SDK/staging_dir/toolchain-mipsel_24kec+dsp_gcc-4.8-linaro_uClibc-0.9.33.2/lib
In a console, type the following commands, and the Paho client for gateway will be compiled.
cd paho.mqtt.c
sudo make
Finally, copy the output files to the gateway. The program is ready for using to publish/subscribe MQTT commands. Users may revise MQTTClient_publish.c/ MQTTClient_subscribe.c to suit your needs.